Climate Change
Our Policy
The Iwatani Group regards climate change and other environmental issues as matters of the highest management concern. We are striving to reduce environmental impact through a wide range of business activities based on the understanding that harmony with the environment is a key prerequisite for corporate survival.
We support the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD).* We use the TCFD framework to assess and identify risks and opportunities associated with climate change; to appropriately verify our response to such risks and opportunities; and to appropriately disclose information.
* In response to a request from G20, the TCFD was established by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) to study matters such as climate-related disclosure.

Governance
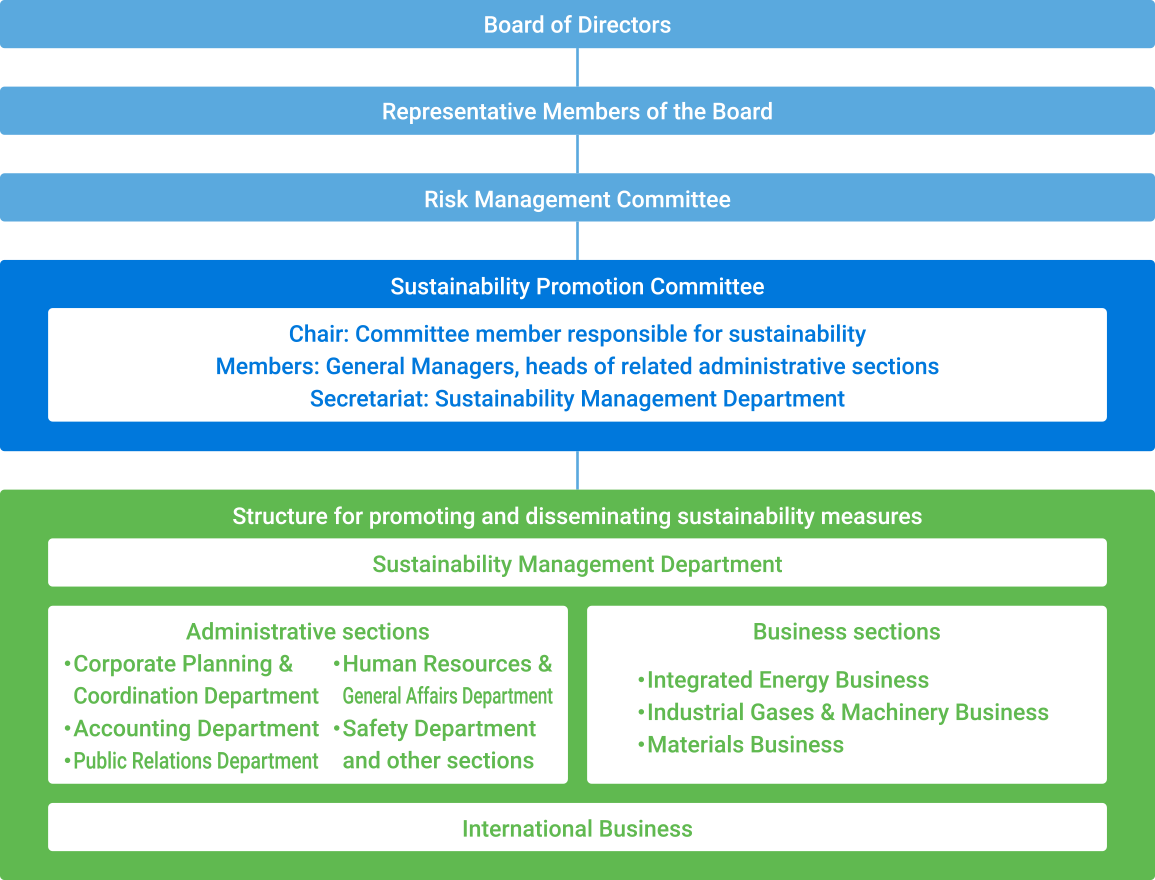
Iwatani has established a Sustainability Management Department. This unit will be responsible for planning measures to promote sustainability and disseminate awareness of sustainability issues throughout the Group, including overseas. Iwatani has also established the Sustainability Promotion Committee under the Risk Management Committee, which coordinates risk management Groupwide. The Sustainability Promotion Committee deliberates on matters such as risks, opportunities, action policies, and targets related to climate change and checks on the progress of related results.
As part of the oversight structure, The Board of Directors receives periodic reports and is also briefed on important matters as they arise to ensure appropriate supervision.
Strategy
Based on our Policy, Iwatani identifies risks and opportunities associated with climate change and analyzes scenarios in line with the recommendations of TCFD. The results are applied in examining medium- to long-term business strategies, making steady progress on initiatives that make our businesses more resilient, and addressing growth opportunities.
As climate change measures move ahead, we recognize the potential for changes in the assumptions underlying our scenarios. Thus, we will continue to update scenarios and analyses as necessary, based on information on scenarios published by external agencies.
Climate Change Risks and Opportunities
By categorizing the various environmental changes associated with climate change into migration risks or physical risks, we seek to assess and identify risks and opportunities for Group businesses in each category.
Risks
| Category | Specific Examples | Time | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transition risks | Policy and legal | Increases in various costs associated with efforts to achieve carbon neutral status
|
Medium to long term |
| Market and reputation | Declining demand for existing products due to growing environmental awareness
|
Medium to long term | |
| Declining demand for natural resources due to growing awareness of recycling | |||
| Technology | Declining demand for LPG and similar energy sources due to the shift toward electrification accompanying advances in storage cell technologies, advances in energy-saving technologies, and other factors | Medium to long term | |
| Progress on hydrogen carrier technologies other than liquid hydrogen (e.g., organic hydrides and ammonia) | |||
| Physical risks | Acute | Supply chain disruptions caused by major natural disasters | Medium to long term |
| Stoppage of production activities | |||
| Rising cost of responding to disasters, repair costs, insurance premiums, etc. | |||
| Chronic | Declining demand for heating and hot-water energy due to global warming | Medium to long term | |
| Poor crop harvests due to changing weather patterns | |||
| Growing cost of responding to rising sea levels | |||
Opportunities
| Category | Specific Examples | Time |
|---|---|---|
| Opportunities related to energy sources | Increasing demand for fuel conversion from heavy oil and similar sources to more eco-friendly LPG and LNG | Short to medium term |
| Growing demand for hydrogen as an alternative to fossil fuels Also, associated growth in hydrogen-related businesses *Growing demand for feasibility studies during the migration period |
Medium to long term *Demand for feasibility studies impacts the short to medium term. |
|
| Widespread use of LPG as a next generation energy source amid the transition to low-carbon and zero-carbon LPG through carbon credits, co-firing of LPG with hydrogen, progress on propanation technologies, and other measures | Medium to long term | |
| Opportunities related to products and services | Growth in sales of products that help reduce environmental impact
|
Short to medium term |
| Increased sales of related fuels alongside growth in the next generation vehicle market | Short to medium term | |
| Growth in CO2 emissions reduction visualization and reduction solutions and in valorization services | Short to medium term | |
| Progress in the Integrated Energy Business on developing cost-competitive delivery and metering systems associated with low CO2 emissions based on progress in AI and IoT technologies and the adoption of related devices, as well as more advanced security and growing opportunities to deliver new value and services | Short to medium term | |
Growth in sales opportunities for products produced through processes associated with low CO2 emissions and cyclical products
|
Medium to long term | |
| Growing use of LPG as a disaster-resistant diversified energy source; growing sales of emergency power generators and other equipment related to business continuity planning (BCP) | Short to medium term | |
| Others | Ability to maintain supply even amid climate change based on the development of a nationwide network of disaster-resilient Core LPG Centers equipped with enhanced seismic resistance, emergency power supplies, and other features | - |
Scenario Analysis
Selecting Businesses for Scenario Analysis
We have chosen the Integrated Energy Business, Industrial Gases & Machinery Business, and Materials Business as the businesses subject to scenario analysis. These businesses are more likely to be affected by climate change.
Definition of Scenarios
In planning scenario analysis, we identified the following two scenarios, based on data and other materials from the International Energy Agency (IEA) and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Both are prestigious international agencies referenced in the TCFD recommendations.
| Scenarios | 4℃ scenario | 2℃ scenario | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potential societal outcomes | In this scenario, society is characterized by economic and social growth accompanied by the continuing extensive development of fossil fuel sources and the continuance of resource- and energy-intensive lifestyles. Average temperatures rise by approximately 4℃ by the end of the century, generating the high likelihood that climate change will affect business activities and results. In this scenario, significant physical impacts will be generated. |
In this scenario, bold policies and technological innovations will be pursued to move toward carbon neutrality and to achieve the ambitious medium- and long-term targets currently advocated by each country. Average temperature increases through the end of this century are kept to less than 2℃. The social changes associated with the transition to a decarbonized society are very likely to affect business activities and results. In this scenario, certain physical impacts will be generated, alongside the significant impact of enhanced regulations and other factors accompanying the transition to a decarbonized society. |
|
| Reference scenarios | Transition | ・Announced Pledges Scenario (IEA WEO 2022) ・Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario (IEA WEO 2022), etc. |
|
| Physical | ・SSP5-8.5 (IPCC AR6), etc. | ・SSP1-2.6 (IPCC AR6), etc. | |
| Main reference parameters | Average global temperatures, sea level rise, frequency of extreme high temperatures on land, frequency of heavy rainfall on land, typhoon damage, labor productivity affected by rising temperatures, etc. | Average global temperatures, sea level rise, frequency of extreme high temperatures on land, frequency of heavy rainfall on land, carbon pricing, electricity pricing, spread of renewable energy, demand for fossil fuels, resource demand, hydrogen demand, etc. | |
Results of Scenario Analysis
Based on a consideration of future market trends and the scenarios identified in the Integrated Energy Business, Industrial Gases & Machinery Business, and Materials Business subjected to scenario analysis, we sought to predict the financial impact in 2050 in relation to the priority factors.
The quantitative information used in scenario analysis is based on scenarios from the IEA, IPCC, and other sources. This information entails numerous uncertainties.
| Financial impact | Large: Equivalent to at least several tens of billions of yen in net sales Moderate: Equivalent to several billions to several tens of billions of yen in net sales Low: Equivalent to several billions of yen in net sales |
|---|
| Scenario | 2℃ scenario | Financial impact | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business | Integrated Energy Business | ||||||||||||||||||
| Timeframe | 2050 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Key risks and opportunities | Risk : Significant decline in demand for fossil fuels due to changing consumer awareness accompanying the adoption of fossil fuel surcharges, emissions credit trading, and other policies and regulations aimed at establishing a decarbonized society. | Large | |||||||||||||||||
| Risk : Widening physical damage to production facilities due to natural disasters | Low | ||||||||||||||||||
| Opportunity : Growing demand for energy-saving equipment—for example, Ene-Farm devices and hybrid water heaters—as awareness of energy conservation and decarbonization grows in the household sector | Moderate | ||||||||||||||||||
| Opportunity : Increased demand for equipment for disaster preparedness accompanying efforts to enhance disaster countermeasures and business continuity planning (BCP) | Low | ||||||||||||||||||
| Opportunity : Major potential business opportunities associated with the development and adoption of green LPG | Large* | ||||||||||||||||||
| *Analysis includes the consequences of measures beyond measurements of the potential impact of climate change under the scenario. | |||||||||||||||||||
| Overview of the anticipated business environment | Under the 2℃ scenario, various factors—for example, sharp tax hikes due to the introduction of carbon taxes or unexpected growth in customers transitioning to non-fossil fuels—may have significant consequences for the Integrated Energy Business, which handles LPG. At the same time, changes may create major business opportunities for the Group, which could be capitalized on by promoting the development and adoption of LPG decarbonization technologies. The changes may also present opportunities for further growth by increasing sales of energy-saving equipment and emergency power supplies and developing the CO2 visualization business and new businesses based on the Iwatani Gateway platform. The 2℃ scenario assumes relatively modest physical impact associated with climate change as of 2050. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Specific measures |
●Taking on the challenges of production and supply of green LPG 1. Participating in feasibility testing to achieve the practical use of green LPG 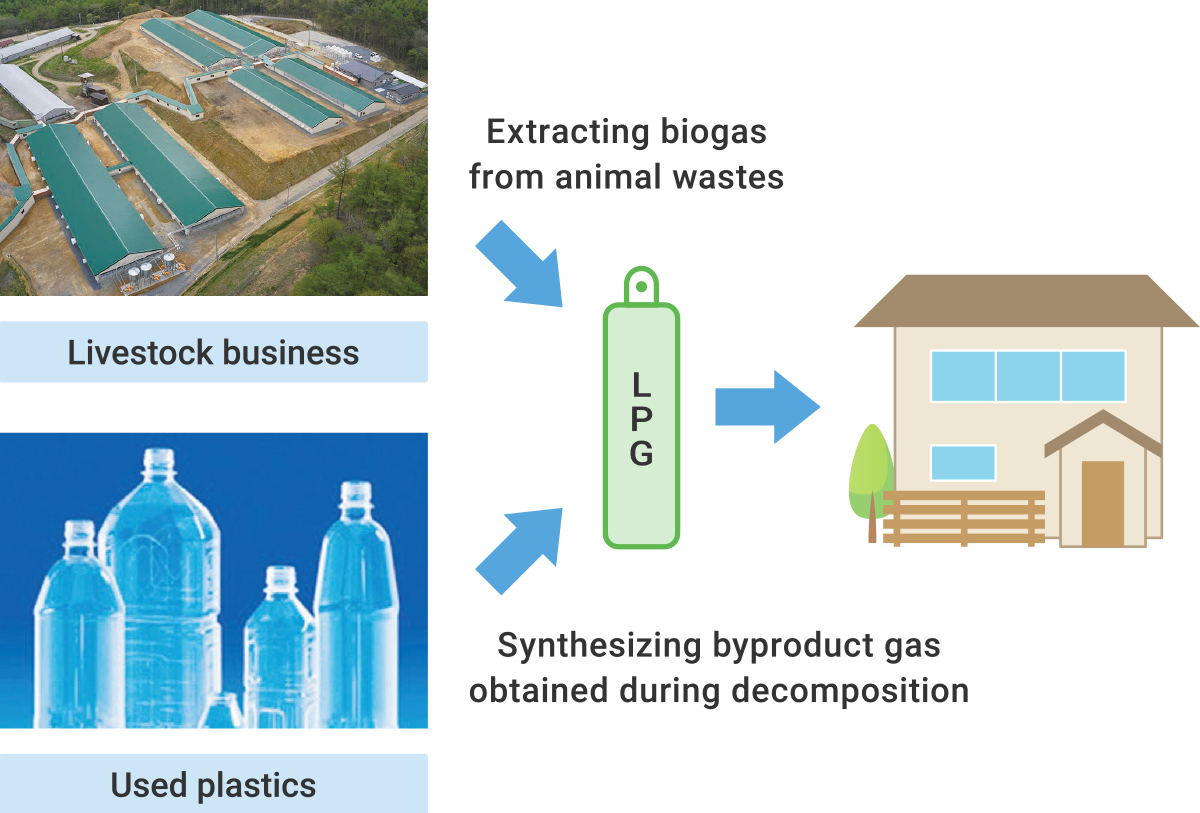 2. Developing green LPG production technologies ●Generating J-Credits from customer CO2 reductions Having registered with the J-Credit program, we are seeking to generate environmental value from the CO2 reductions achieved by customers who have switched to fuels like LPG and LNG. We coordinate customer CO2 emissions reductions and apply for certification under the J-Credit program. This program makes it possible to convert CO2 reduction activities into environmental value. 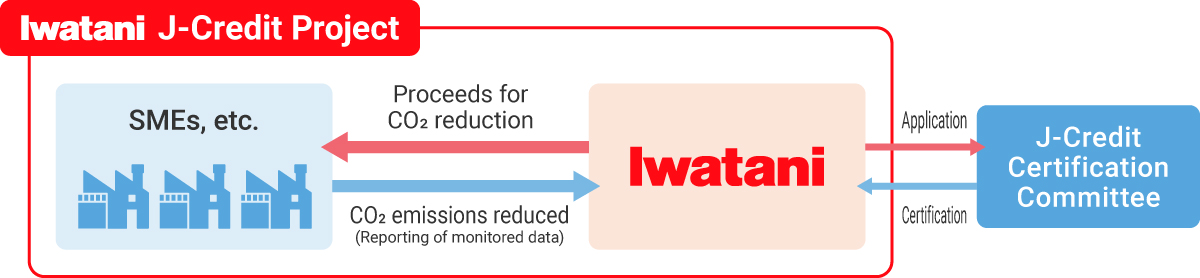 ●Launching efforts to quantify and assign value to the CO2-reduction effects of high-efficiency gas water heaters in ordinary households Employing blockchain technologies, this initiative will ensure tamper-resistance and traceability by collecting data on gas used by gas water heaters through Iwatani Gateway, our proprietary IoT platform. This in turn will make it possible to assign a value (J-Credits) to CO2 reductions at households using high-efficiency gas water heaters. 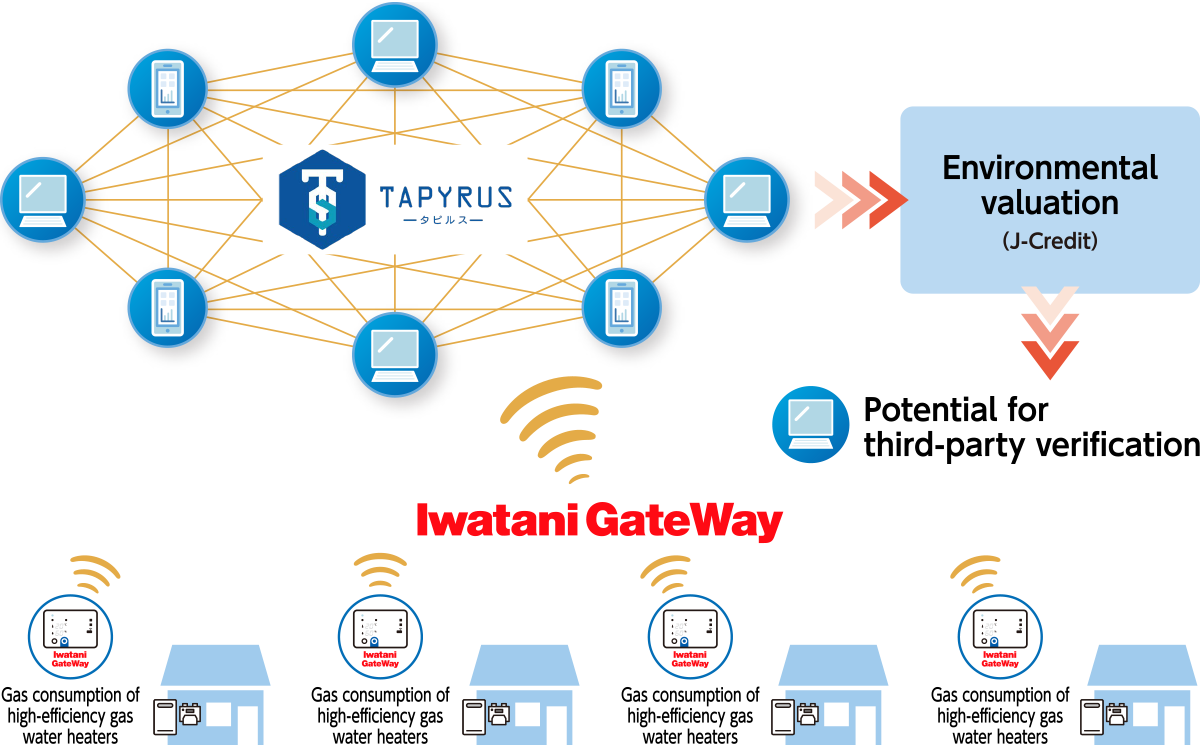 ●Hydrogen-LPG mixed pipeline supply Together with Soma Gas Co., Ltd. and other partners, Iwatani has been selected to participate in the following NEDO* contracted projects: Technology Development Project for Building a Hydrogen-based Society/Technology Development for Hydrogen Utilization in the Community/Study of Potential for Hydrogen Production and Utilization. *NEDO: New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization 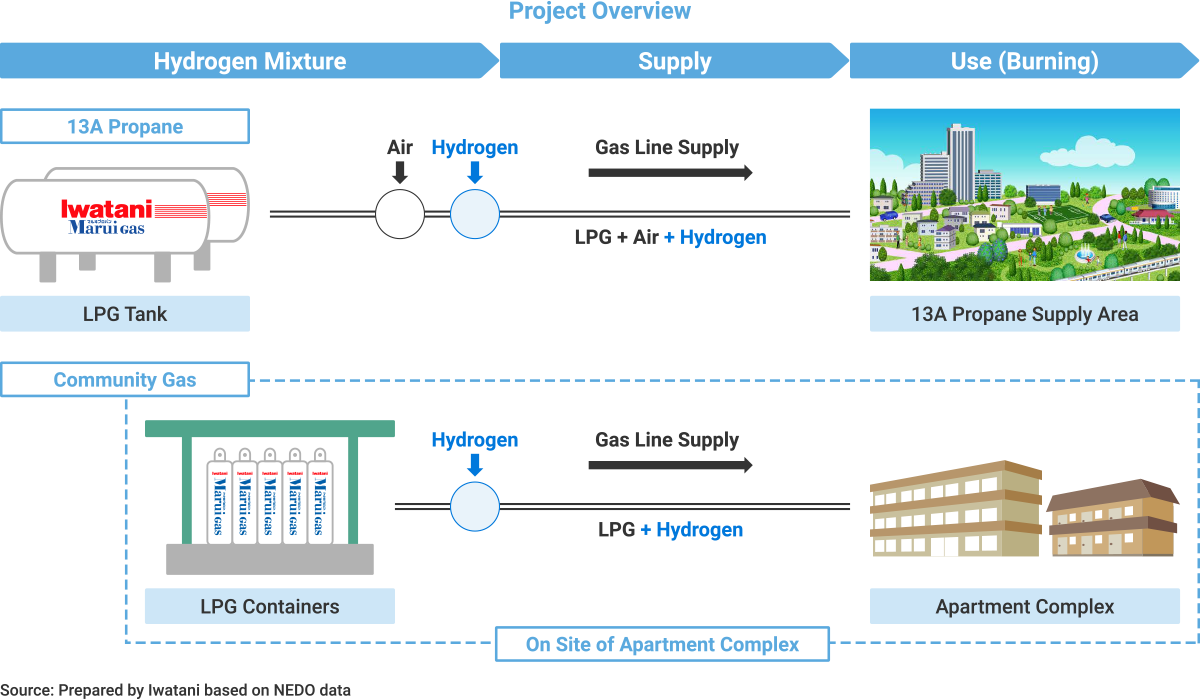 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Financial information |
Financial information on the Integrated Energy Business
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Scenario | 2℃ scenario | Financial impact | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business | Industrial Gases & Machinery Business | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Timeline | 2050 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key risks and opportunities | Risk : Higher costs for electricity and decarbonization measures at industrial gas plants with the growing adoption of carbon taxes, emissions credit trading, and other policies and regulations | Moderate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Risk : Widening physical damage to production facilities due to natural disasters | Low | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opportunity : Large-scale growth in both domestic and international demand for hydrogen, mainly as a fossil fuel alternative; significant growth in demand for hydrogen-related equipment as hydrogen demand grows | Large* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| *There is potential for very high growth opportunities depending on the extent of progress on addressing climate change. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview of the anticipated business environment | While the 2℃ scenario assumes higher costs for electricity and decarbonization measures at industrial gas plants, as carbon taxes and other policies are adopted progressively, it also presents the potential for rapid growth in the hydrogen business due to sharp growth in demand for hydrogen as a fossil fuel alternative; for use as a raw material for various synthetic energy fuels; and for use in other applications. In addition, steady demand growth is expected for various industrial gases such as oxygen, nitrogen, argon, and helium to parallel economic growth. The 2℃ scenario assumes relatively modest physical impact associated with climate change as of 2050. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specific measures |
To establish a hydrogen energy-based society, we are partnering with government agencies and numerous private sector businesses to build supply chains for CO2-free hydrogen and to enhance engineering functions. ●Liquid hydrogen supply chain commercialization feasibility study project In February 2022, feasibility testing of sea transport and the loading/unloading of liquid hydrogen between Australia and Japan via liquid hydrogen tankers—part of a NEDO demonstration project—met with success. To move closer to the full-fledged implementation of a CO2-free hydrogen supply chain, we have been granted subsidies from the Green Innovation Fund to establish the world’s first hydrogen liquefaction and transport technologies on the scale of tens of thousands of tons annually and test an integrated international liquid hydrogen supply chain that ranges from hydrogen production through liquefaction, shipping, sea transport, and unloading. Given the need to reduce costs by scaling up facilities for commercialization in FY2030 and beyond, plans call for the tankers used in this project to be at least 100 times larger than that used in the feasibility testing described above.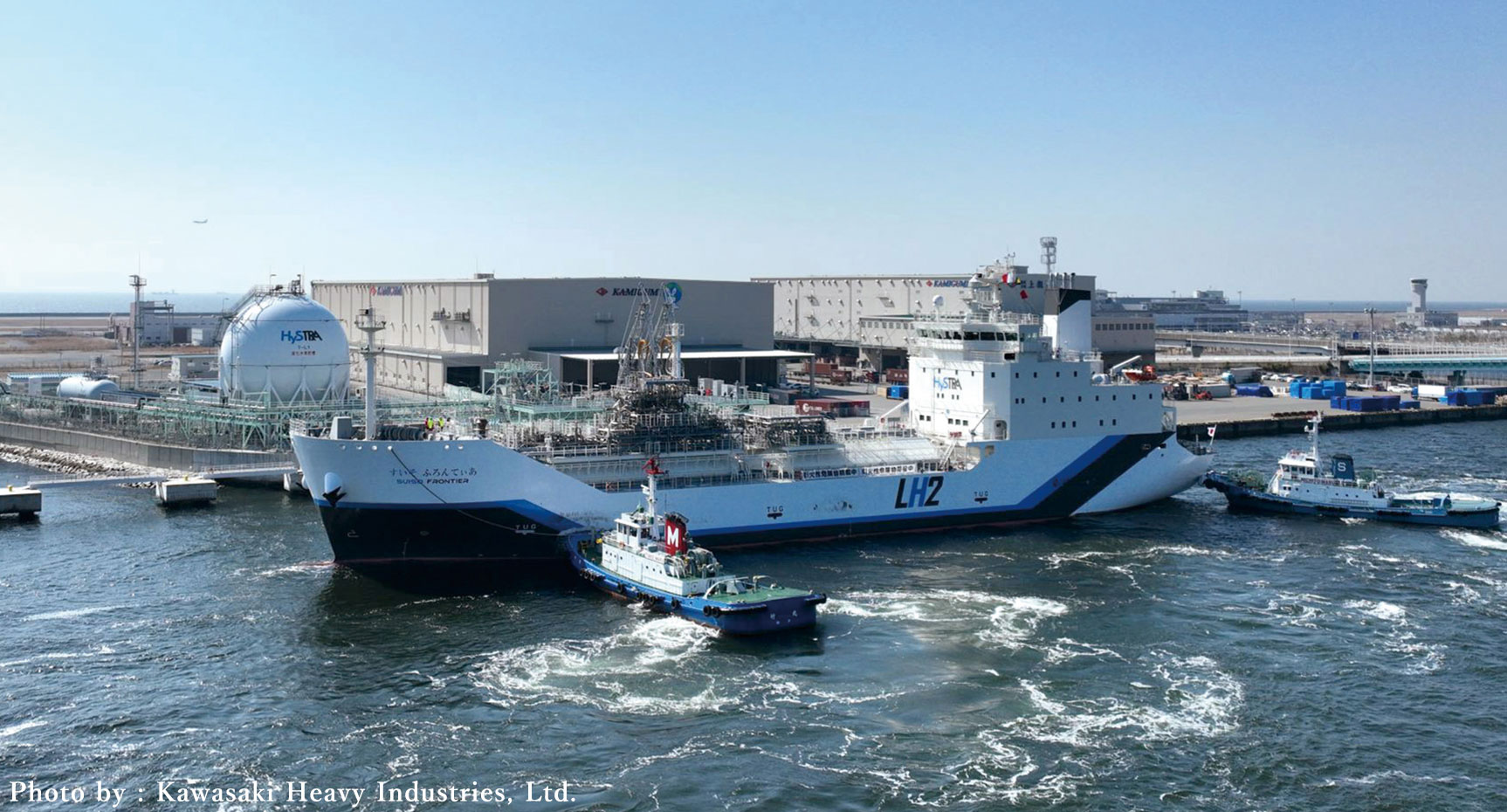  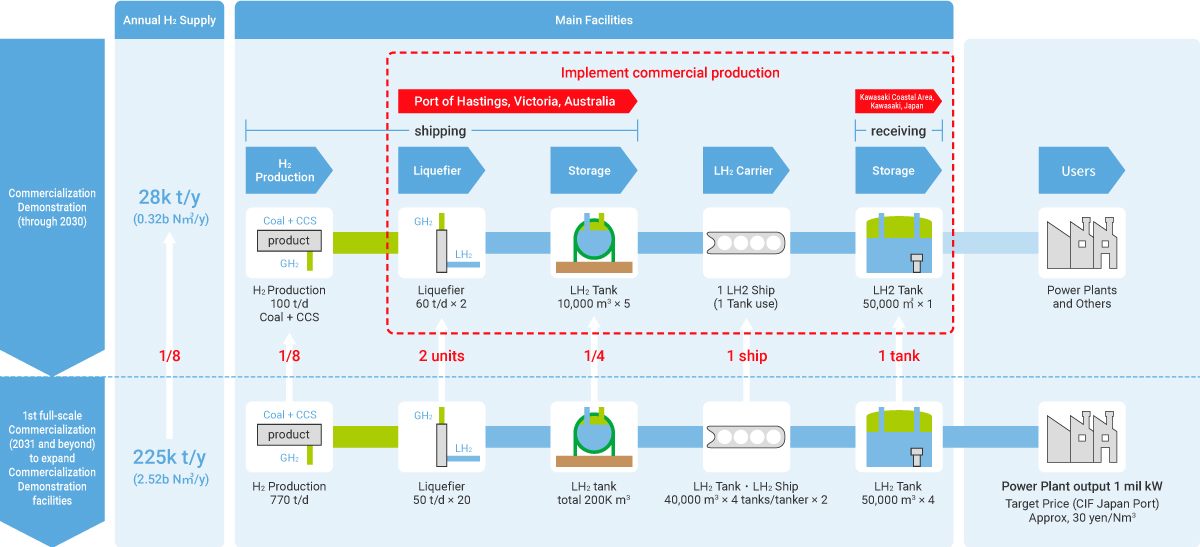 ●Enhancing engineering functions; joint efforts in hydrogen-refueling station business and other businesses We are striving to enhance manufacturing and engineering functions. We made Tokico System Solutions, Ltd. a wholly-owned subsidiary. Tokico System Solutions, Ltd. offers strengths in energy supply facilities, including hydrogen dispensers for fuel cell vehicles (FCVs).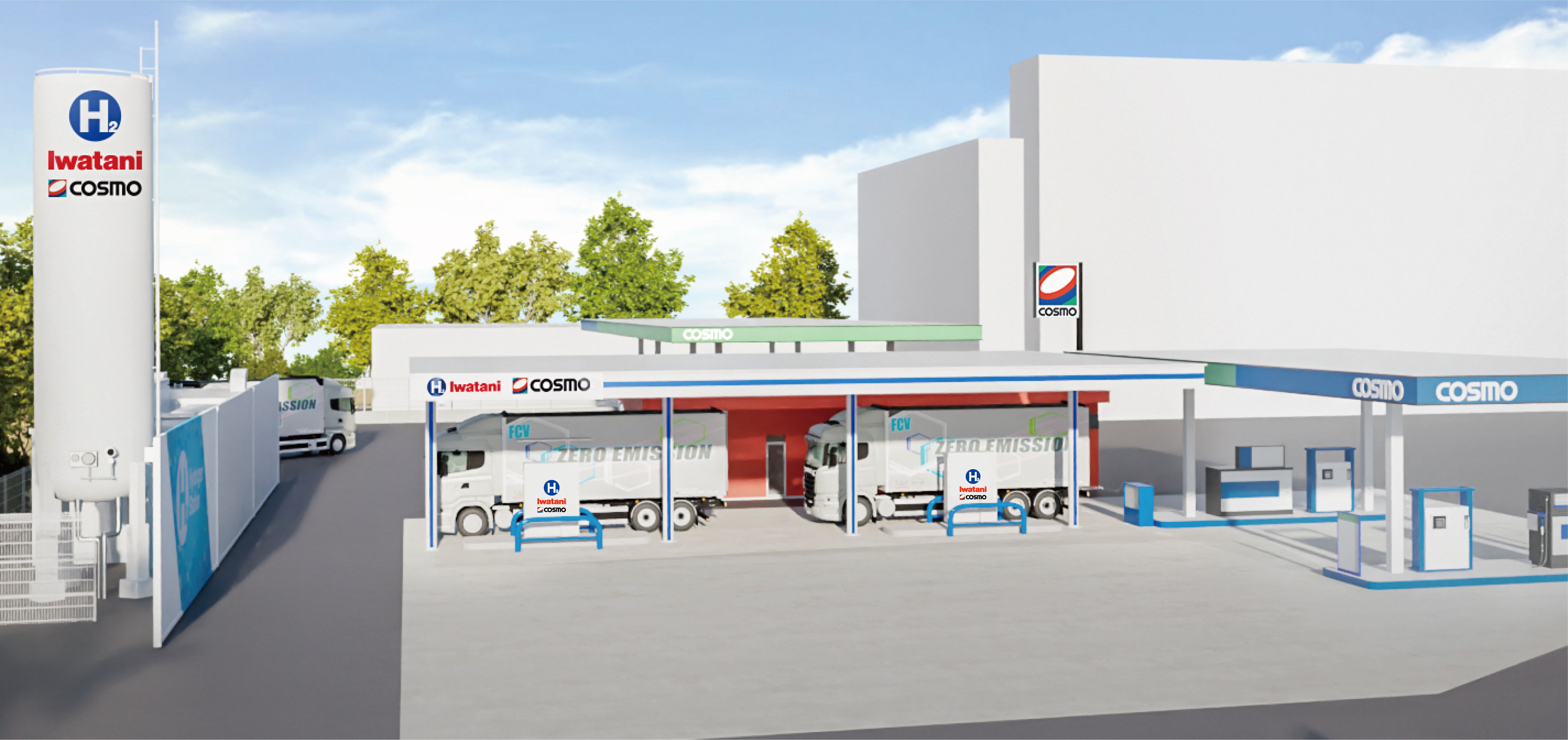  ●Mixed-hydrogen burners, hydrogen cutting machines Iwatani has developed and launched the sale of hydrogen cutting machines that cut steel sheet using 100% hydrogen gas. Replacing the acetylene and LPG traditionally used in machinery for cutting steel girders and thick steel sheet used in construction machinery and other products with 100% hydrogen gas will make it possible to eliminate all CO2 emissions generated by cutting. 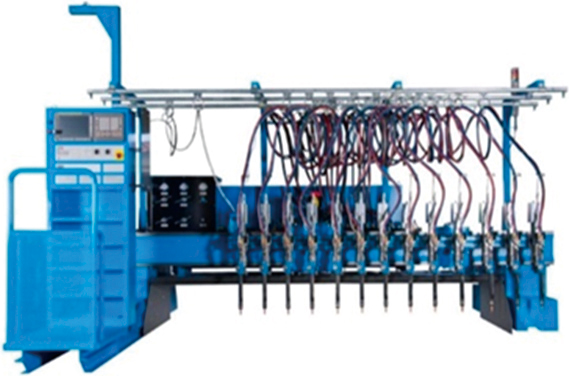  |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial information |
Financial information on the Industrial Gases & Machinery Business
Financial and other information on the hydrogen business
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scenario | 2℃ scenario | Financial impact | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business | Materials Business | ||||||||||||||||||
| Timeframe | 2050 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Key risks and opportunities | Risk : Higher costs for electricity and decarbonization measures, mainly in the resource and metal processing businesses, with the growing adoption of carbon taxes, emissions credit trading, and other policies and regulations | Moderate | |||||||||||||||||
| Risk : Widening physical damage to production facilities due to natural disasters | Low | ||||||||||||||||||
| Opportunity : Growing demand for lithium, cobalt, and other rechargeable battery materials with growing use of EVs and stationary batteries | Large | ||||||||||||||||||
| Opportunity : Growth in the metal processing business for air conditioners in response to the growing use of home air conditioners mainly in emerging markets, as well as the switch to electric heating systems and shift to energy-efficient models | Moderate | ||||||||||||||||||
| Opportunity : Growing demand for PKS, wood pellets, and other biomass fuels as alternatives to fossil fuels | Moderate | ||||||||||||||||||
| Overview of the anticipated business environment | The 2℃ scenario assumes higher costs for electricity and decarbonization measures, mainly in the resource and metal processing businesses, as carbon taxes and other policies are adopted progressively. On the other hand, it also raises the possibility of growing demand for rechargeable battery materials and biomass fuels and expanding opportunities in the business of processing metals for air conditioner use. In addition, it raises the possibility of further growth through the development and promotion of business activities related to 100% biomass PET resins, biodegradable resins, and plastic recycling. The 2℃ scenario assumes relatively modest physical impact associated with climate change as of 2050. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Specific measures |
●Initiatives related to rechargeable battery materials to meet EV-related demand Iwatani imports and sells materials, including lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, for cathode active materials in lithium ion rechargeable batteries, which show promise for next generation vehicle applications. 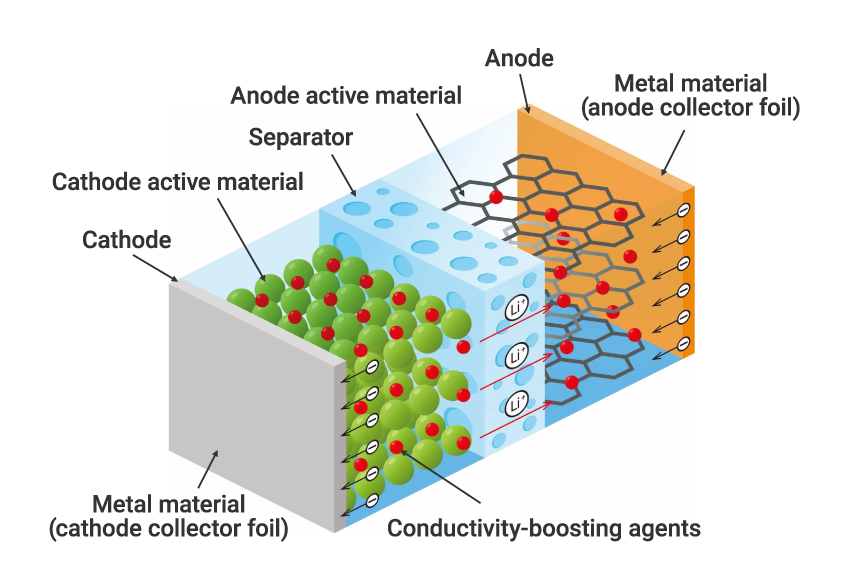 Cathode active materials
●Expansion of processing plant for metals (wire) materials used in air conditioners Since its founding in 1990, Bangkok Ai-Toa Co., Ltd. has expanded, primarily through sales in Southeast Asia, North America, and Europe. It manufactures metal fan guards used in air conditioners, dishwasher baskets, oven racks, and other parts for use in kitchen appliances, as well as auto parts, logistics equipment, and other products.  In the air conditioner field in particular, markets are expected to continue to grow in Southeast Asia, Europe, India, and other regions. The market for air-to-water (ATW) air-source heat pumps is projected to grow in Europe, North America, and elsewhere. ●Eco-Friendly PET Resins Iwatani is actively developing and deploying PET resins that have low environmental impact. We have developed and brought to market biomass resin, a plastic made by replacing monoethylene glycol, which accounts for 30% of all raw materials in conventional resins, with plant sourced materials. We have also developed a highly recyclable aluminum catalyst resin that has been adopted as a new resin to promote PET recycling. We are also planning to introduce aluminum catalyst biomass resins that take advantage of the features of both biomass resin and aluminum catalyst resin to realize both reduced CO2 emissions and high recycling rates. 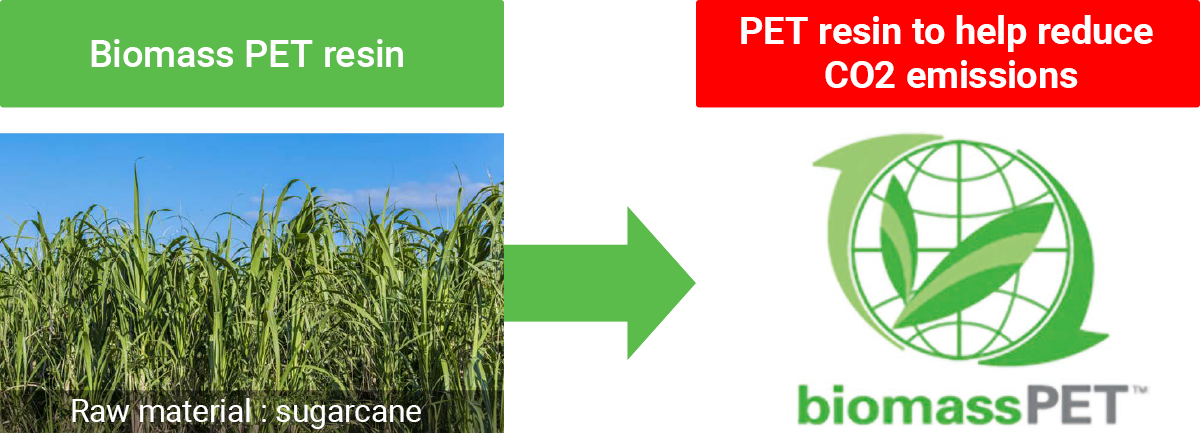 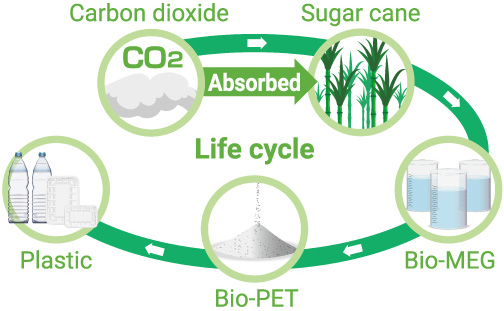 ●Plastic chemical recycling business (R Plus Japan) In June 2020, R Plus Japan, Ltd., a company for used plastics recycling established by Iwatani and 11 other companies in the plastic value chain, launched operations. Harnessing recycling technologies developed by US biochemical startup Anellotech Inc., the company applies chemical methods to recycle plastics, including PET bottles, directly into raw materials. This method requires fewer steps than conventional methods and helps minimize CO2 emissions and energy use. To help identify solutions to plastics issues, R Plus Japan is currently working to commercialize its recycling technologies by 2027. 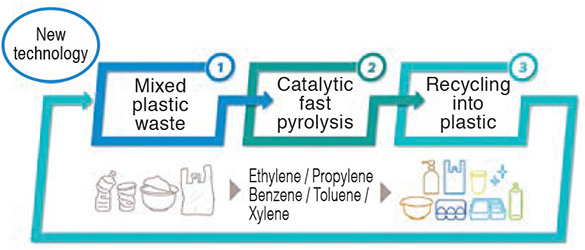 ●Securing rights to high-purity titanium ore mined using electricity from renewable energy (hydroelectric) By investing in Nordic Mining ASA, the Norwegian resources firm, we have secured rights for the Japanese market to high-purity titanium ore from a new mining concession slated to begin operating in 2024. After Australia, this will be the second site of our mineral sands business. This measure will contribute to reliable access to important minerals. The high-purity titanium ore used in aircraft parts and other applications is rare and characterized by low production volumes around the world. This project marks a pioneering global step in green titanium materials mining and achieves zero CO2 emissions in various ways, including use of electricity from renewable energy (hydroelectric).  |
||||||||||||||||||
| Financial information |
Financial information on the Materials Business
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Scenario | 4℃ scenario | Financial impact | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business | All businesses | ||
| Timeframe | 2050 | ||
| Key risks and opportunities | Risk : Lower LPG sales due to rising temperatures | Low | |
| Risk : Higher costs of responding to disasters | Low | ||
| Risk : Lower productivity due to rising temperatures | Moderate | ||
| Risk : Increased loss of profits due to growing frequency of disasters | Low | ||
| Opportunity : Higher sales of disaster response and BCP equipment, including LPG-powered emergency generators | Low | ||
| Overview of the anticipated business environment | The 4℃ scenario assumes higher acute risks, which bring sudden damage (e.g., higher costs of responding to disasters, increased loss of profits due to disaster events), and higher chronic risks, which have ongoing and chronic impacts on business activities (e.g., lower production, lower LPG sales volumes). At all production and filling facilities, our LPG and industrial gas businesses identify maximum flooding risk levels based on hazard maps published by local governments and implement the necessary countermeasures. In addition to physical countermeasures, we strive to strengthen the maintenance of BCP manuals, undertake disaster drills, and promote safety awareness through everyday safety activities. Having established the only nationwide disaster relief team in the private sector energy industry, the LPG business strives to maintain and strengthen its disaster response capabilities. We are also at work installing LPG-powered emergency generators and auto gas-filling facilities at major sites. We believe we have achieved a degree of risk resilience even under the 4℃ scenario. |
||
| Specific measures |
●Developing energy infrastructures to support the community We operate the industry’s leading supply network to ensure that customers across Japan can rely on their LPG supply lines. This network includes five import terminals, 114 filling stations, and some 140 distribution centers. Additionally, we are enhancing facilities at filling stations across Japan to ensure a stable supply of LPG, even in the event of natural disasters. In addition to the seismic retrofitting of the LPG storage and filling facilities at our 64 Core LPG Centers across Japan, we are enhancing LPG emergency power generators and autogas filling equipment to maintain functionality in the event of power failures. 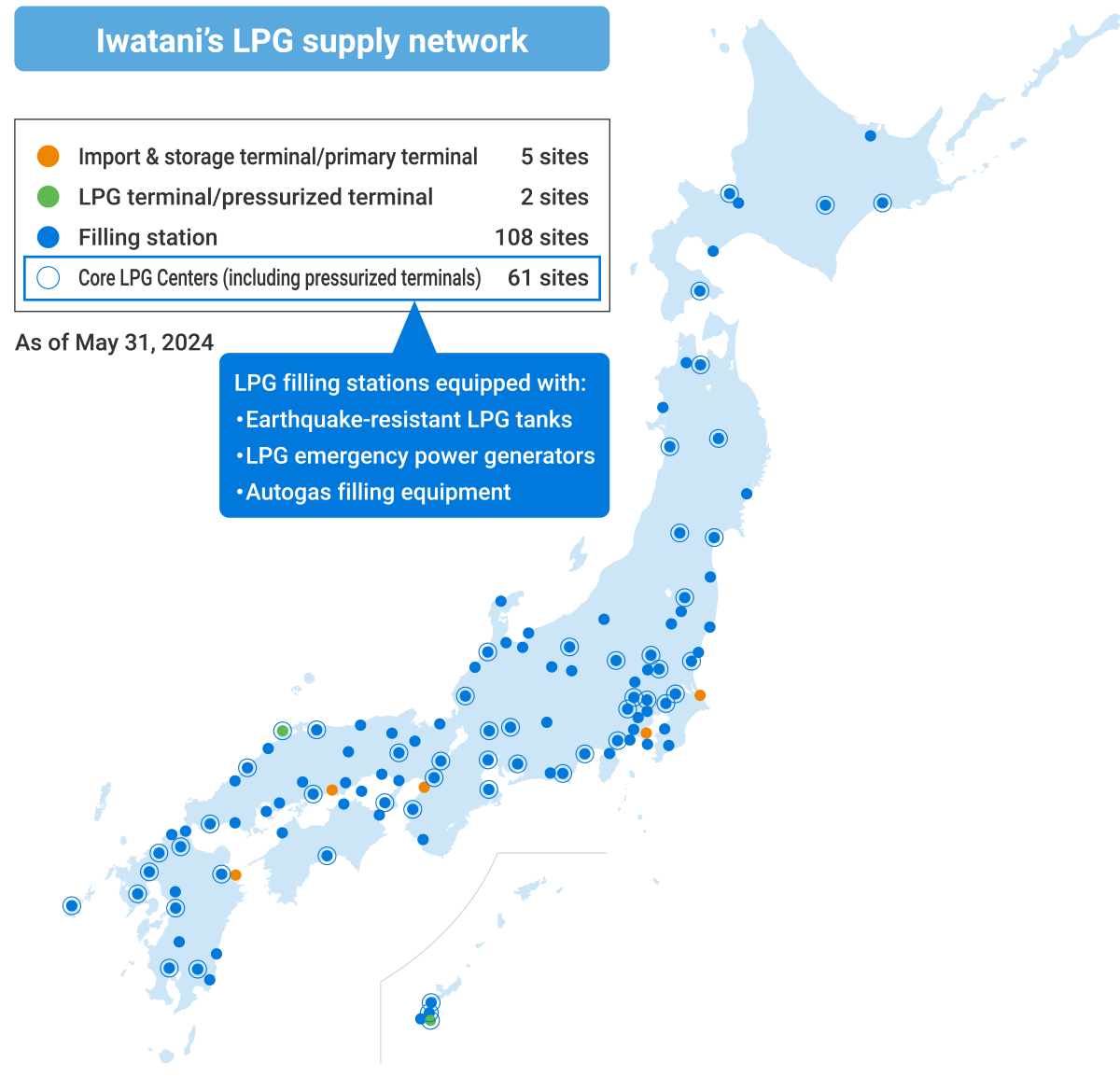 ●MaruiGas Disaster Relief Corps Established jointly with some 1,400 MaruiGas distributors to ensure rapid LPG recovery in response to disasters, the MaruiGas Disaster Relief Corps is Japan’s largest and most unique nationwide private sector disaster prevention organization. Deployment examples
●A supply chain to support the stable supply of helium Helium, an essential material for MRIs in the medical field and in state-of-the-art fields such as fiber optics and semiconductors, is a rare natural resource produced in only a few countries. We achieve a stable supply of helium through double sourcing from the two countries of Qatar and the United States. We operate production facilities not just in Japan, where we boast the leading market share, but in China, Singapore, Thailand, and Qatar. This ensures a stable supply not just to the domestic market, but to emerging helium markets in China, Southeast Asia, and elsewhere. 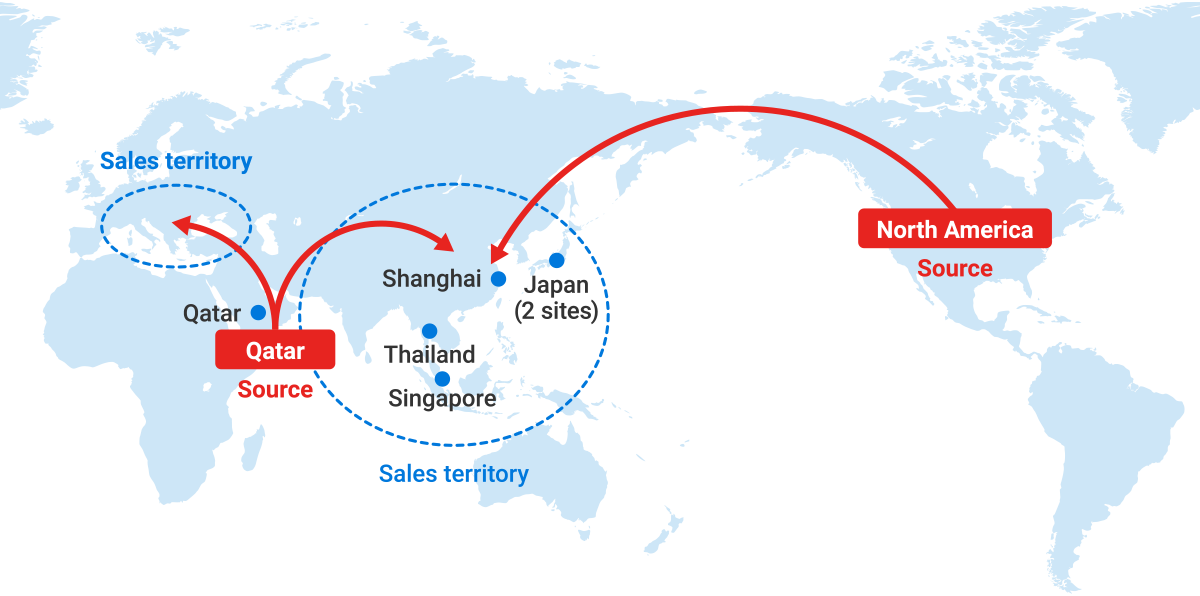 |
||
Risk Management
The Iwatani Group has established a Risk Management Committee to ensure integrated management of risks across all Group companies. As part of its comprehensive risk measures, it has also established a Sustainability Promotion Committee and other specialized committees under the Risk Management Committee to address key risks related to compliance, plant safety, and other matters.
The Risk Management Committee holds regular meetings overseen by the chairperson and strives to manage risks Groupwide, including risks related to compliance with applicable laws and regulations. Special individual committees also meet regularly to monitor the status of compliance and efforts related to these risks, reporting on the matters discussed to the Risk Management Committee.

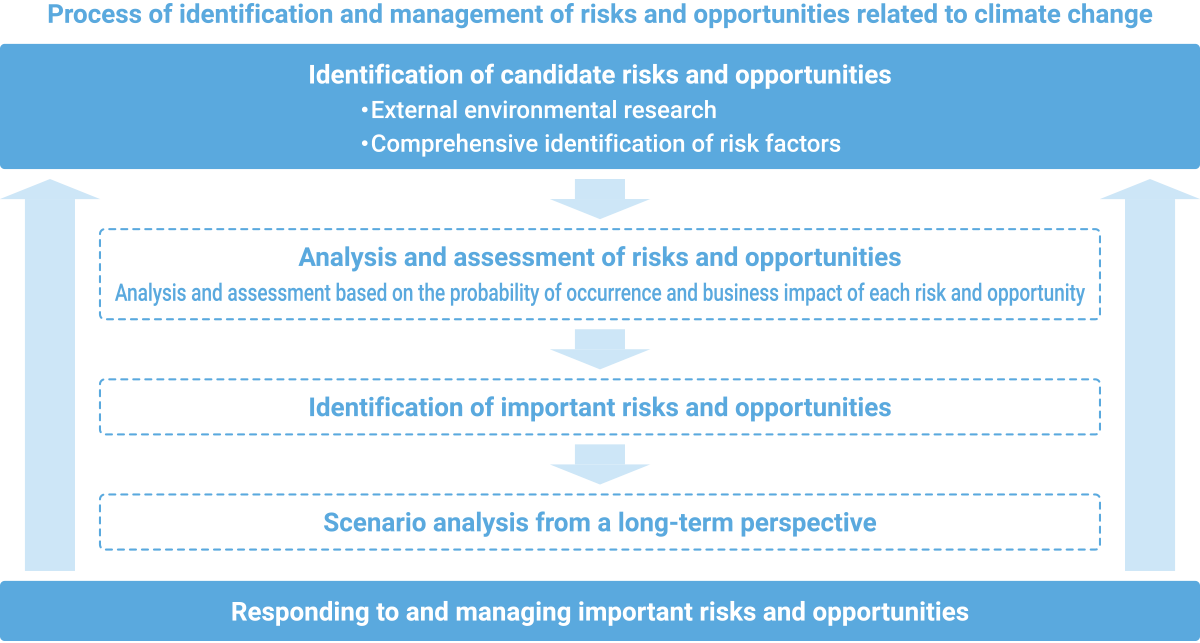
We are proceeding with efforts to strengthen our response to climate change risks and our efforts to address climate change opportunities by assessing these risks and opportunities along the two axes of probability of occurrence and impact on business.
In addition, we assess the business impact of climate change in stages, based on the extent of the potential financial impact. In particular, we assess the future business environment via scenario analysis from a long-term perspective and in light of the unique characteristics of climate change.
Metrics & Targets
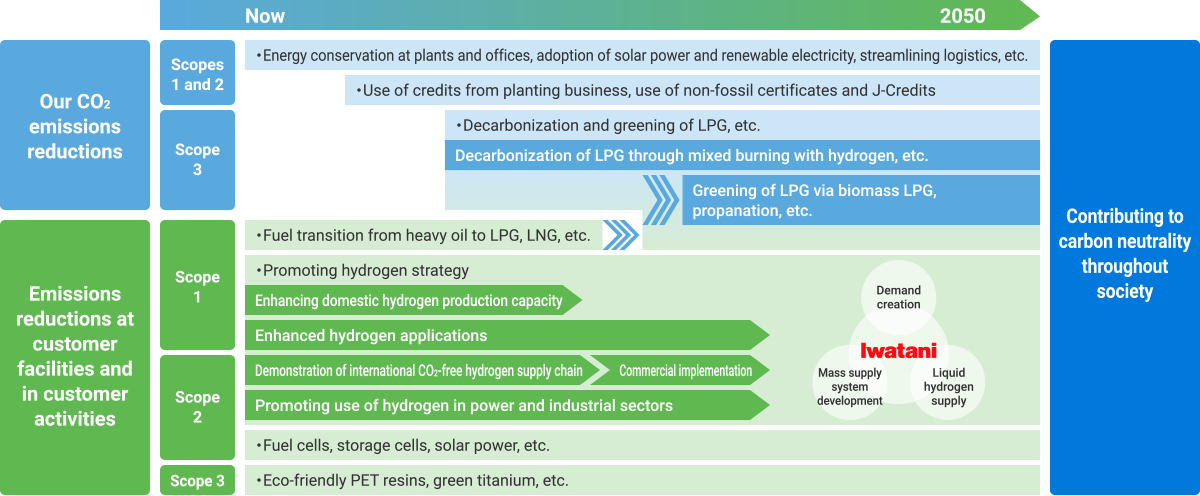
The Iwatani Group has announced its goal of achieving carbon neutrality by FY2050, targeting as a milestone to be reached by FY2030 reductions of 50% in CO2 emissions compared to FY2019 levels by the Iwatani Group in Japan.
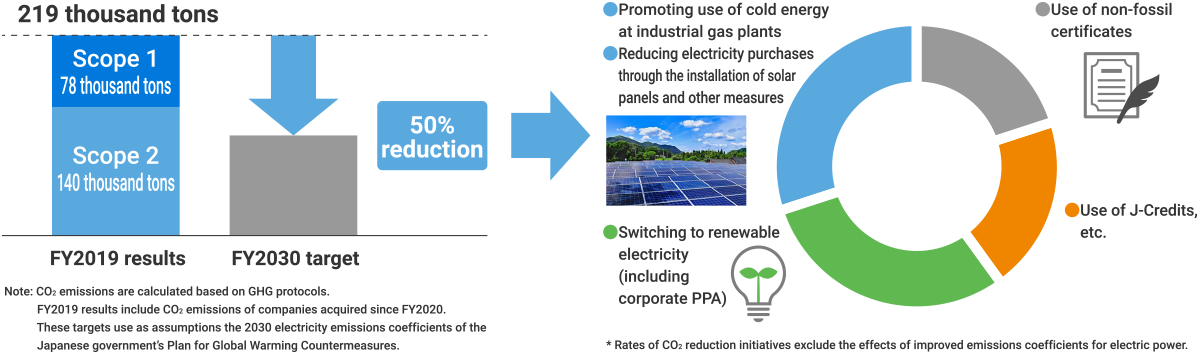
We aim to achieve our reduction targets for FY2030 through various measures, including the utilization of unused cold energy and the installation of solar panels at industrial gas plants; switching to renewable energy, including corporate PPA; and applying J-Credits that we ourselves generate. Where reductions are difficult, we will consider use of non-fossil fuel certificates.
To achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, we will reduce CO2 emissions in our business activities and contribute to the reduction of CO2 emissions in society as a whole through the expansion of our hydrogen and other businesses.