Machinery / Environment
Chemical Adsorption Deodorizer
The chemical adsorption type deodorizer "Bellaria," which has achieved unprecedented adsorption capacity, uses a deodorizing material made of magnesium hydrous silicate (natural porous clay) as its main ingredient, with unique formulations for each target odor substance.
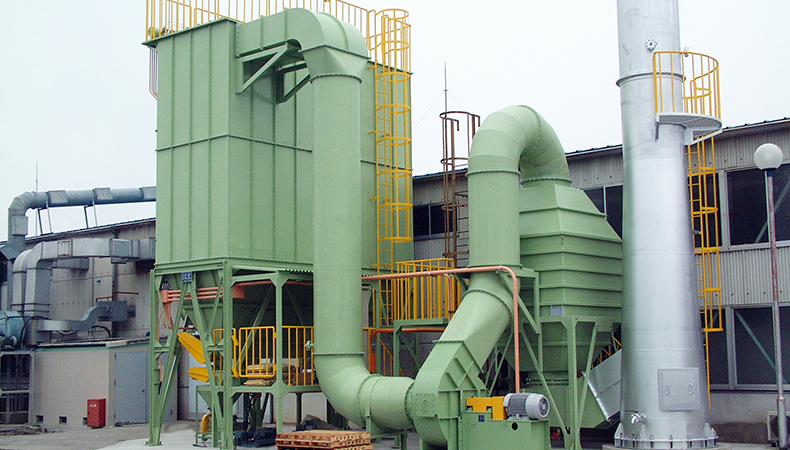
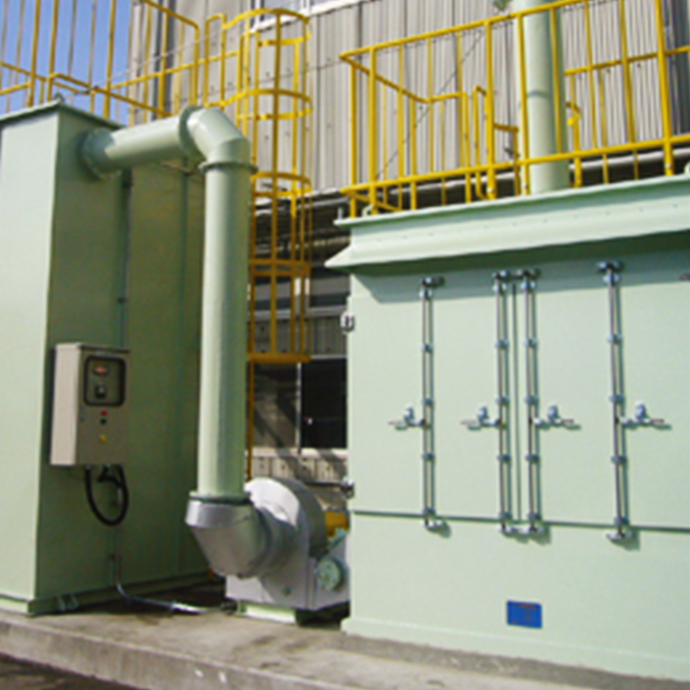


Features
- Recyclable at the plant and can be used over and over again, thus eliminating waste.
- Because it chemically adsorbs malodorous substances, even small molecules can be captured, and there is no need to heat the reaction field (energy saving).
- The honeycomb-shaped cassette system makes it easy to replace the cassette.
- Low pressure loss due to good air permeability saves on equipment and electricity costs (energy saving).
- The large surface area efficiently cools the reaction heat generated during adsorption.
- Highly flammable and safe due to porous ceramics as the main component
Comparison Between Chemical Adsorption and Activated Carbon (Physical Adsorption)
Chemical Adsorption
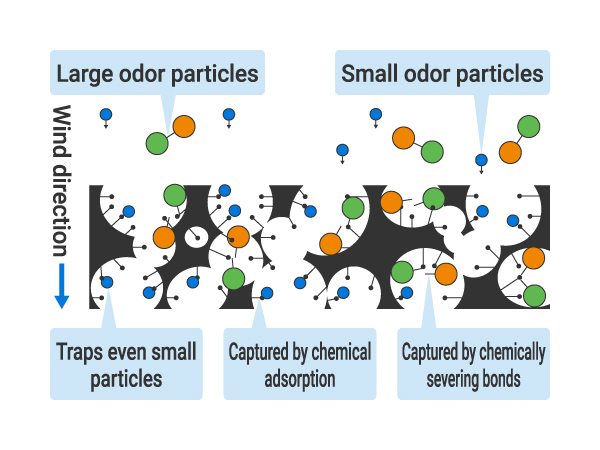
- Captured by chemical reaction
- Capable of trapping even small molecules
- Chemical bonds keep them together
- Large molecules can be chemically decomposed and adsorbed
Physical Adsorption
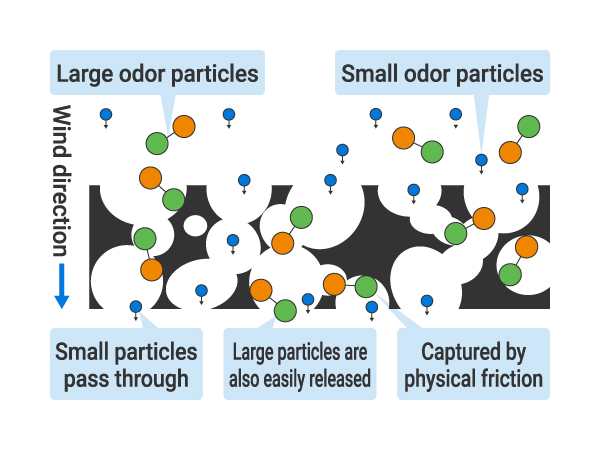
Source: Izumi Environmental Engineering Co., Ltd.
- Trapped by friction on the hole wall
- Small molecules cannot be trapped
- Friction traps them so they can easily separate from each other
- Larger molecules remain intact
Comparison of pressure characteristics with activated carbon (Physical Adsorption)
In the case of granular activated carbon, partial blockage of process gas and velocity distribution within the packing layer can easily occur, and pressure loss is also high, so a honeycomb structure is used in this system. The honeycomb structure has a large contact area, making the equipment compact and enabling uniform adsorption through reduced pressure loss and uniform velocity distribution. The large contact area with the outside air also provides excellent dissipation of adsorption heat.
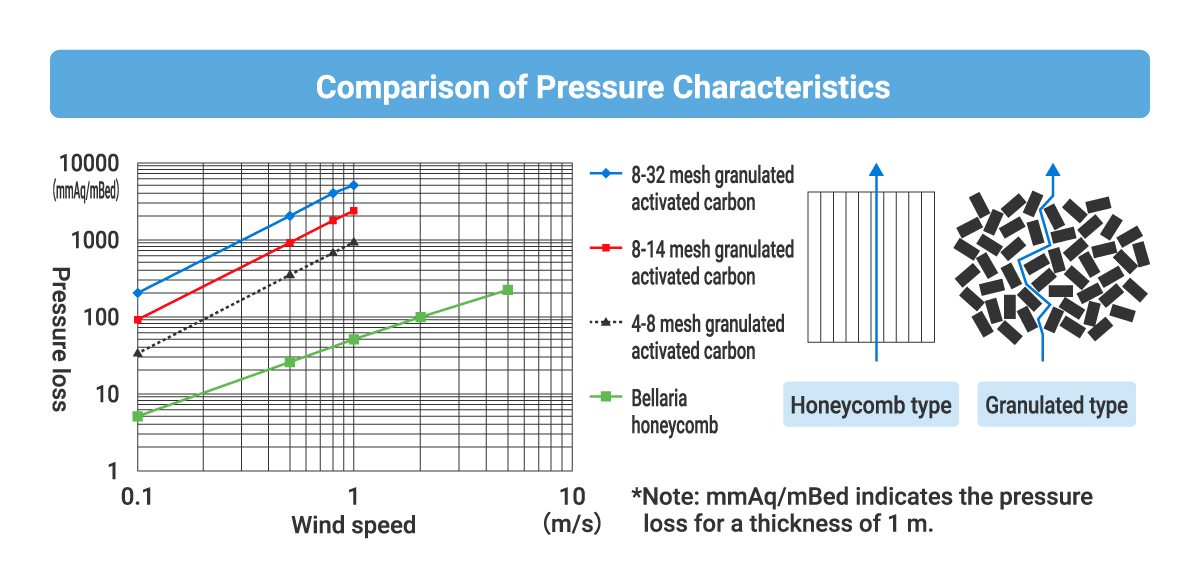
Source: Izumi Environmental Engineering Co., Ltd.
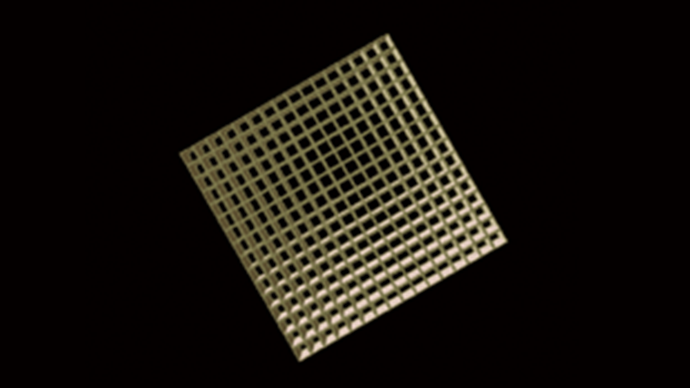
Honeycomb Appearance
Honeycomb Viewed from Above
List of Actual Applications
- Chemical Industry
Plastics plants (organic solvents, additives), synthetic rubber plants (organic solvents, sulfur compounds), printing/ink plants (organic solvents), pharmaceutical plants (organic solvents, sulfides), agrochemical plants (ammonia), adhesive manufacturing plants (organic solvents) - General Manufacturing Industry
Cigarette manufacturing plants (amines, nitrogen compounds aldehydes), foundries (amines, ammonia), furniture plants (organic solvents) - Livestock, Fertilizer, and Feed Industry
Fertilizer manufacturing plants (ammonia, sulfur compounds), feed manufacturing plants (ammonia, amines, sulfur compounds), fish meal processing plants (ammonia, amines, sulfur compounds), pig/cattle/poultry farms (sulfur compounds, amines, lower fatty acids) - Food Manufacturing Industry
Livestock plants (sulfur compounds, ammonia, lower fatty acids), seafood manufacturing plants (sulfur compounds, amines, nitrogen compounds), oil/fat-based food manufacturing plants (lower fatty acids, aldehydes), starch manufacturing plants (sulfur compounds, nitrogen compounds, lower fatty acids) - Other Industries
Waste disposal plants (sulfur compounds, amines, organic solvents), sewage treatment plants (sulfur compounds, amines, ammonia), refuse collection sites (sulfur compounds, amines, organic solvents)
Please inquire for more information on environmental systems.
Environmental Equipment Department
Tokyo
81-3-5405-5811
Osaka
81-6-7637-3181
